Electric
power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an
electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt, one joule per
second. Electric power is usually produced by electric generators, but
can also be supplied by sources such as electric batteries.
- Distribution Systems can be defined as the sequential flow of procedures, systems, and activities which are designed and linked to facilitate and monitor the movement of goods and services from the source to the consumer.
- Electric-power transmission is the bulk transfer of electrical energy, from generating power plants to electrical substations located near demand centers. This is distinct from the local wiring between high-voltage substations and customers, which is typically referred to as electric power distribution.
 |
| Typical Power Transmission and Distribution Scenario |
- Electric power is normally generated at 11-25kV in a power station. To transmit over long distances, it is then stepped-up to 400kV, 220kV or 132kV as necessary. Power is carried through a transmission network of high voltage lines.
- Usually, these lines run into hundreds of kilometres and deliver the power into a common power pool called the grid. The grid is connected to load centres (cities) through a sub-transmission network of normally 33kV (or sometimes 66kV) lines. These lines terminate into a 33kV (or 66kV) substation, where the voltage is stepped-down to 11kV for power distribution to load points through a distribution network of lines at 11kV and lower.
- At these load points, a transformer further reduces the voltage from 11kV to 415V to provide the last-mile connection through 415V feeders (also called as Low Tension (LT) feeders) to individual customers, either at 240V (as single-phase supply) or at 415V (as three-phase supply).
- A feeder could be either an overhead line or an underground cable. In urban areas, owing to the density of customers, the length of an 11kV feeder is generally up to 3 km. On the other hand, in rural areas, the feeder length is much larger (up to 20 km). A 415V feeder should normally be restricted to about 0.5-1.0 km. Unduly long feeders lead to low voltage at the consumer end.
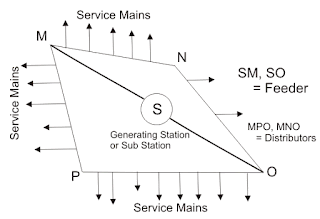 |
| LINE DIAGRAM OF POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM |
The main function of an electrical power distribution system is to provide power to individual consumer premises. Distribution of electric power to different consumers is done with much low voltage level.
Distribution of electric power is done by distribution networks. Distribution networks consist of following main parts.
- Distribution substation,
- Primary distribution feeder,
- Distribution Transformer,
- Distributors,
- Service mains. .
POWER DISTRIBUTION ANIMATION





